The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), enacted in May 2018, marked a significant shift in how companies handle personal data in the European Union. It set a high standard for data protection and privacy, compelling businesses worldwide to reevaluate their data practices. For marketers, the implications are profound, especially regarding compliance costs. Understanding the financial impact of non-compliance is crucial for organizations striving to maintain their marketing budgets.
The Financial Stakes of Non-Compliance
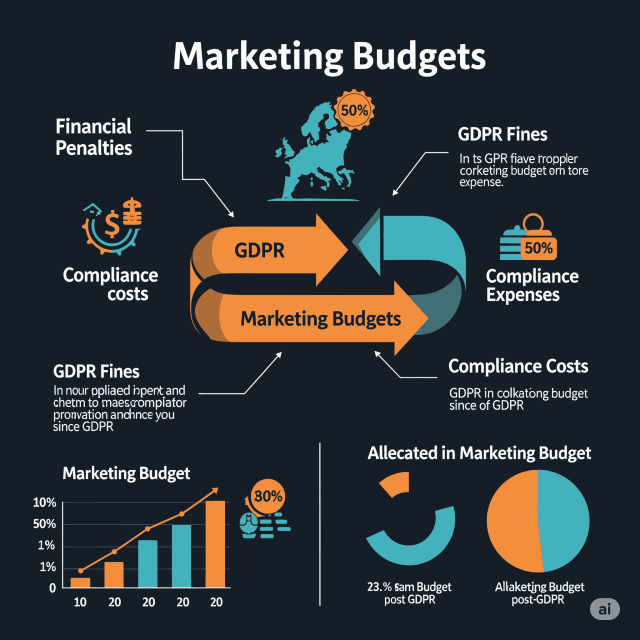
Non-compliance with GDPR can lead to hefty fines—up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher. This financial risk isn’t just a possibility; cases have already emerged where companies faced massive fines due to lapses in GDPR compliance. For instance, British Airways was fined £20 million for a data breach affecting 400,000 customers, a stark reminder of the financial repercussions that can arise from negligence.
Besides fines, companies risk reputational damage, which can lead to decreased sales and customer trust. The cost of rebuilding a brand image can be substantial, far exceeding the initial compliance costs.
Impact on Marketing Budgets
Increased Compliance Costs
Marketing departments must allocate a portion of their budgets to ensure compliance with GDPR. This includes investing in:
- Data Protection Officers (DPOs): Hiring or designating a DPO who oversees data protection strategy and implementation.
- Legal Consultation: Engaging legal experts to navigate complex regulations and ensure that marketing practices align with GDPR.
- Technology and Tools: Investing in secure data management systems, consent management platforms, and customer relationship management (CRM) tools designed for compliance.
Training and Awareness
Employee training is another area where marketing budgets are impacted. Teams must understand data protection principles, including data minimization, purpose limitation, and the importance of obtaining explicit consent. Training sessions and workshops can incur significant costs but are essential for fostering a culture of compliance.
Marketing Strategies Adjustments
GDPR necessitates a reevaluation of marketing strategies. Marketers must shift from traditional approaches to more transparent practices. This may involve redesigning campaigns to ensure data collection aligns with GDPR principles, which can lead to increased operational costs. Companies might need to focus on:
- Opt-in Marketing Strategies: Creating campaigns that require explicit consent from users, which may limit potential customer reach compared to broader opt-out strategies.
- Privacy-First Messaging: Adopting communication that emphasizes data protection can resonate well with consumers but may require additional resources for development and distribution.
Potential Loss of Competitive Edge
Non-compliance can lead to delayed marketing initiatives due to the need for redesigns and internal audits. In fast-paced industries, this lag could mean missing out on market opportunities and falling behind competitors who have adapted more swiftly to GDPR requirements.
The Long-Term Benefits of Compliance
While the upfront costs of GDPR compliance may seem daunting, companies can gain long-term advantages by investing in robust data protection measures. Compliance fosters consumer trust, enhancing brand loyalty and customer retention. In an increasingly privacy-conscious marketplace, businesses that prioritize data protection may find themselves at a competitive advantage.
Enhanced Customer Relationships
By ensuring transparent communication and safeguarding customer data, companies can build stronger relationships with their audiences. Satisfied customers are more likely to engage with and promote brands they trust, leading to improved sales and ROI.
Innovation and Efficiency
Implementing GDPR-compliant systems can streamline data management processes, making them more efficient. This can lead to innovation in marketing strategies and a more targeted approach, optimizing the marketing budget in the long run.
Conclusion
The cost of non-compliance with GDPR is multi-faceted, affecting marketing budgets and overall business health. Companies need to view compliance not as a burden but as an investment in their future. By proactively addressing GDPR requirements and embedding data protection into their marketing strategies, organizations can mitigate risks, enhance customer trust, and ultimately drive long-term growth. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, prioritizing compliance will be crucial for staying competitive and relevant.