In today’s data-driven world, understanding how marketing efforts translate into customer actions is crucial for any business aiming to maximize its return on investment (ROI). Enter marketing attribution models—frameworks designed to analyze the contribution of various channels in the customer journey. With several models to choose from, businesses often face a significant challenge in selecting the most appropriate one. This article will explore the different marketing attribution models available and help you determine which is right for your business.
What is Marketing Attribution?
Marketing attribution refers to the process of assigning credit to different marketing channels or touchpoints that lead to a conversion. By understanding which channels drive engagement, leads, and sales, businesses can optimize their marketing strategies, allocate budgets effectively, and ultimately improve their performance.
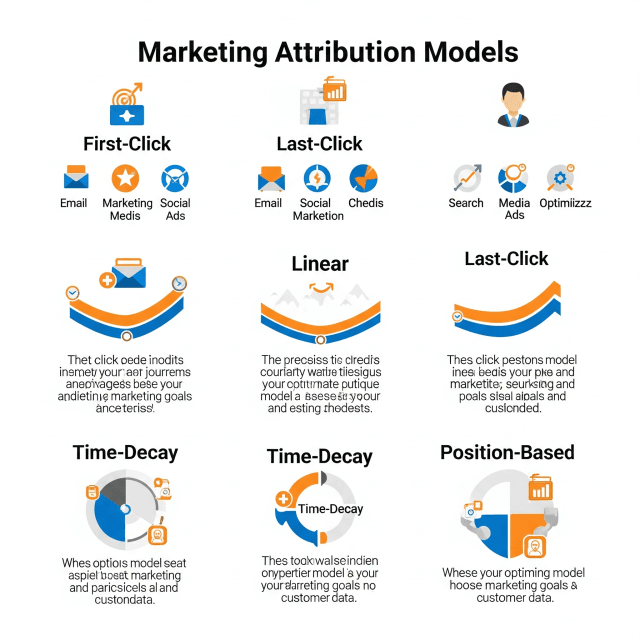
Types of Marketing Attribution Models
Several attribution models are widely used in the industry, each with its own unique approach and methodology. Here are the most recognized models:
1. Last Click Attribution
Overview: This model attributes 100% of the conversion credit to the last channel a customer interacted with before making a purchase.
Pros:
- Simple and easy to implement.
- Provides clear insights into which channels close sales.
Cons:
- Ignores the influence of earlier touchpoints in the customer journey.
- May lead to misplaced budget allocations.
Best for: Businesses with straightforward sales processes and a focus on immediate conversion.
2. First Click Attribution
Overview: Opposite to last click, this model gives all credit to the first channel that initiated the customer journey.
Pros:
- Useful for understanding awareness-driven campaigns.
- Highlights the effectiveness of initial touchpoints.
Cons:
- Similarly neglects the role of subsequent interactions.
- May misrepresent overall channel effectiveness.
Best for: Brands looking to boost awareness and understand lead generation channels.
3. Linear Attribution
Overview: This model evenly distributes credit across all touchpoints in the customer journey.
Pros:
- Gives a balanced view of the entire customer journey.
- Encourages a diverse marketing strategy.
Cons:
- Oversimplifies the complexities of consumer behavior.
- May dilute the importance of high-performing channels.
Best for: Businesses with multi-channel strategies that want a comprehensive look at their marketing effectiveness.
4. Time Decay Attribution
Overview: This model gives more credit to touchpoints that are closer in time to the conversion event, acknowledging that recent interactions are often more influential.
Pros:
- Offers a more realistic view of customer behavior.
- Recognizes the importance of nurturing leads over time.
Cons:
- Can complicate analysis and reporting.
- Might still undervalue early-stage interactions.
Best for: Businesses with longer sales cycles or those that require multiple interactions before conversion.
5. Position-Based Attribution
Overview: This model attributes 40% of the credit to the first and last interactions, with the remaining 20% distributed among the middle touchpoints.
Pros:
- Highlights the significance of both the initial and closing interactions.
- Acknowledges the full journey while placing importance on key moments.
Cons:
- More complex to implement than simpler models.
- May still perpetuate misallocations if middle touchpoints are undervalued.
Best for: Businesses that want to focus on both awareness and conversion, such as those with lengthy purchase decisions.
6. Data-Driven Attribution
Overview: This sophisticated model uses algorithms to distribute credit based on actual data and customer interactions, allowing for a more customized analysis.
Pros:
- Tailor-fitted to your specific customer behavior and market conditions.
- Provides insights that evolve over time with changing trends.
Cons:
- Requires advanced analytics tools and expertise.
- Often involves a higher initial investment in data management.
Best for: Larger organizations with access to extensive data and the resources to analyze it effectively.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
When selecting a marketing attribution model, consider the following:
Sales Cycle Length: Shorter sales cycles may benefit from last-click or first-click models, while longer cycles might necessitate time decay or data-driven models.
Marketing Channels: Analyze the variety of channels you utilize. A diverse strategy may call for linear or position-based models to capture all interactions.
Goals and Objectives: Determine what you aim to measure—are you focused on awareness or conversions? This will guide your model selection.
Data Availability: Assess the amount of data you have and the tools at your disposal. If you lack comprehensive data, simpler models may be more practical.
- Resources for Interpretation: Consider whether you have the expertise in-house to interpret data accurately. For complex models, professional assistance may be necessary.
Conclusion
Marketing attribution is a vital component of a successful business strategy in the digital era. By understanding the various attribution models available and aligning them with your business goals, you can make informed decisions that enhance your marketing efforts. Whether you choose a simple approach or a complex, data-driven method, the key is to continually assess and refine your chosen model to ensure it meets the evolving needs of your business.